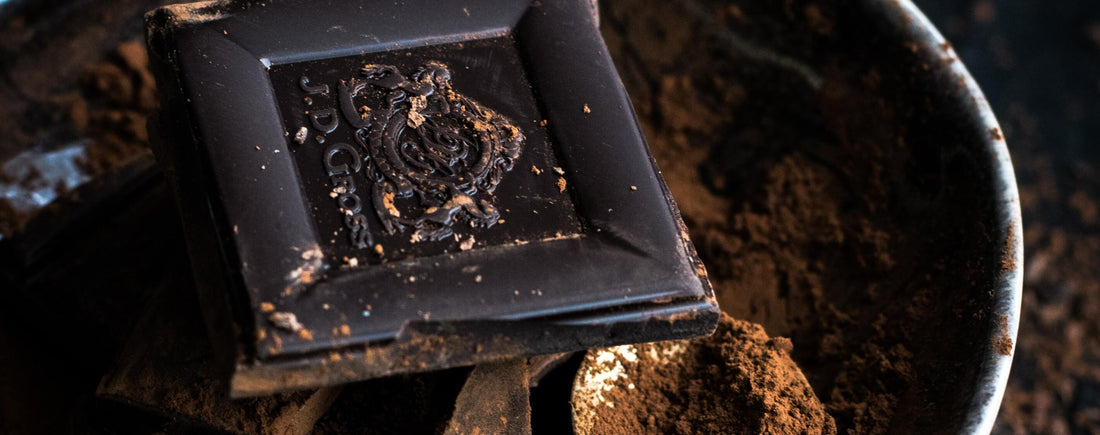
Do you love chocolate? What if you could eat it every day for your health? Eating chocolate every day might sound too good to be true, but research shows that there are some excellent health gains associated with eating dark chocolate. There are, however, also some potential risks.
Before we look at the health benefits and risks of dark chocolate, let’s take a look at how dark chocolate is made.
Cocoa pods mature on the vine and are hand-harvested, then cut open to dry. The cocoa beans, covered in a white pulp, are laid out in the sun to ferment, and the chocolate flavor starts to emerge. Different types of fermentation processes result in different flavors of chocolate. The dried beans are then cracked open, the shells are removed, and the remaining cocoa nibs are roasted.
The roasting process also affects the flavor of the cocoa nibs. Roasted nibs are ground into a liquid called cocoa liquor, which is free of alcohol and contains 50 to 60 percent cocoa butter. From there the cocoa liquor can be further refined into cocoa powder, or other ingredients like sugar, vanilla, nuts, fruits, or milk can be added to the cocoa liquor to make chocolate bars.
Dark chocolate contains 60 percent or more cocoa, and no milk. Milk chocolate only contains 5 to 7 percent cocoa, and white chocolate doesn’t contain any cocoa at all—just cocoa butter and milk. As with berries and leafy greens, the darker the color of the chocolate, the more antioxidant properties it contains and the better it is for you. Also, milk binds to the antioxidants eliminating their ability to fight free radicals, so eating milk chocolate or drinking milk with dark chocolate has few to no health benefits.
Dark chocolate contains polyphenols, a powerful type of antioxidant that is also found in foods like berries, green and black tea, and red wine. These polyphenols help to defend the body’s cells against free radicals from environmental toxins and diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and chronic inflammation. In fact, one study by Yale University Prevention Research Center indicated that chocolate contains more phenolic antioxidants than any other food.
Studies done at the University of Southern California, the Institute of Cardiology in Russia, and the University of Guadalajara, Mexico, showed that consumption of dark chocolate helps improve blood flow, lower blood pressure, lowers LDL blood cholesterol (bad cholesterol), increases HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol), improves vascular function, and reduces the risk of stroke. According to a study of overweight men done at Wageningen University in the Netherlands, consuming dark chocolate daily for four weeks helped restore flexibility to arteries while also preventing white blood cells from sticking to the walls of blood vessels. This is significant because arterial rigidity and white blood cell adhesion are both factors in heart disease.
The same study mentioned above by Yale University Prevention Research Center showed that dark chocolate has significant positive effects on cognitive function in the brain. Results from a study done in the UK confirmed that eating dark chocolate provides an acute improvement in visual and cognitive functions. A study done at Swinburne University in Melbourne, Australia, revealed “significantly increased self-rated calmness and contentedness relative to placebo” in participants who consumed a dark-chocolate drink mix for 30 days.
Dark chocolate is a mineral powerhouse. One ounce of dark chocolate—recommended daily serving—contains the following daily recommended doses of minerals: copper (25 percent), calcium (2 percent), iron (19 percent), magnesium (16 percent), potassium (6 percent), and zinc (6 percent).
Phytochemicals in dark chocolate have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Just keep an eye on the sugar content, as sugar is an inflammatory food. To get the most anti-inflammatory benefits from chocolate, go for the high cocoa content and least amount of sugar.
New research from Queen Margaret University in the U.K. shows that dark chocolate improves insulin sensitivity and reduced insulin resistance by decreasing glucose levels in non-diabetic adults.
It Contains Caffeine
Dark chocolate contains 35 milligrams of caffeine per ounce compared to 145 milligrams for an 8-ounce cup of black coffee. Consider that if you’re trying to watch your caffeine intake or not hinder your ability to fall asleep at night.
It Can Increase the Risk of Kidney Stones
Dark chocolate contains a component found in many plants and animals called oxalates, which can increase the risk of kidney stones. If you’re prone to getting kidney stones you may want to watch your dark chocolate consumption.
It Can Bring on Migraines
Dark chocolate has been implicated in some migraines. However, there are also people who are prone to migraines and don’t seem to be affected by dark chocolate, so the jury is still out. If you have a tendency to get migraines you may want to cut dark chocolate out of your diet to see if it helps.
Consult your healthcare practitioner if you’re concerned about caffeine, kidney stones, or migraines. For the best dark chocolate, shop at local chocolatiers, and buy organic and/or fair-trade whenever possible.
*Editor’s Note: The information in this article is intended for your educational use only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and before undertaking any diet, supplement, fitness, or other health programs.
Ready to take control of your health? Download the Chopra App for personalized well-being guidance you can access anywhere.
Before we look at the health benefits and risks of dark chocolate, let’s take a look at how dark chocolate is made.
From Bean to Bar
Chocolate is made from cocoa beans that grow on cacao trees, originally native to Central America and now grown in tropical climates throughout the world. A single cacao tree produces 20 to 30 cocoa pods per year, and each pod contains around 40 cocoa beans. It takes one year’s yield from a single tree to produce about five dark chocolate bars.Cocoa pods mature on the vine and are hand-harvested, then cut open to dry. The cocoa beans, covered in a white pulp, are laid out in the sun to ferment, and the chocolate flavor starts to emerge. Different types of fermentation processes result in different flavors of chocolate. The dried beans are then cracked open, the shells are removed, and the remaining cocoa nibs are roasted.
The roasting process also affects the flavor of the cocoa nibs. Roasted nibs are ground into a liquid called cocoa liquor, which is free of alcohol and contains 50 to 60 percent cocoa butter. From there the cocoa liquor can be further refined into cocoa powder, or other ingredients like sugar, vanilla, nuts, fruits, or milk can be added to the cocoa liquor to make chocolate bars.
Dark chocolate contains 60 percent or more cocoa, and no milk. Milk chocolate only contains 5 to 7 percent cocoa, and white chocolate doesn’t contain any cocoa at all—just cocoa butter and milk. As with berries and leafy greens, the darker the color of the chocolate, the more antioxidant properties it contains and the better it is for you. Also, milk binds to the antioxidants eliminating their ability to fight free radicals, so eating milk chocolate or drinking milk with dark chocolate has few to no health benefits.
Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate
Chocolate has been used for its healing properties for more than 3,000 years, and dates back to the early Mayans. Now researchers are finding scientific evidence for those healing properties.Dark chocolate contains polyphenols, a powerful type of antioxidant that is also found in foods like berries, green and black tea, and red wine. These polyphenols help to defend the body’s cells against free radicals from environmental toxins and diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and chronic inflammation. In fact, one study by Yale University Prevention Research Center indicated that chocolate contains more phenolic antioxidants than any other food.
It’s Good for the Circulatory System
Studies done at the University of Southern California, the Institute of Cardiology in Russia, and the University of Guadalajara, Mexico, showed that consumption of dark chocolate helps improve blood flow, lower blood pressure, lowers LDL blood cholesterol (bad cholesterol), increases HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol), improves vascular function, and reduces the risk of stroke. According to a study of overweight men done at Wageningen University in the Netherlands, consuming dark chocolate daily for four weeks helped restore flexibility to arteries while also preventing white blood cells from sticking to the walls of blood vessels. This is significant because arterial rigidity and white blood cell adhesion are both factors in heart disease.
It’s Good for Brain Cognition and Your Mood
The same study mentioned above by Yale University Prevention Research Center showed that dark chocolate has significant positive effects on cognitive function in the brain. Results from a study done in the UK confirmed that eating dark chocolate provides an acute improvement in visual and cognitive functions. A study done at Swinburne University in Melbourne, Australia, revealed “significantly increased self-rated calmness and contentedness relative to placebo” in participants who consumed a dark-chocolate drink mix for 30 days.
It’s High in Minerals
Dark chocolate is a mineral powerhouse. One ounce of dark chocolate—recommended daily serving—contains the following daily recommended doses of minerals: copper (25 percent), calcium (2 percent), iron (19 percent), magnesium (16 percent), potassium (6 percent), and zinc (6 percent).
It Has Anti-inflammatory Properties
Phytochemicals in dark chocolate have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Just keep an eye on the sugar content, as sugar is an inflammatory food. To get the most anti-inflammatory benefits from chocolate, go for the high cocoa content and least amount of sugar.
It Improves Insulin Sensitivity
New research from Queen Margaret University in the U.K. shows that dark chocolate improves insulin sensitivity and reduced insulin resistance by decreasing glucose levels in non-diabetic adults.
Health Risks of Eating Dark Chocolate
Although there are many great health benefits of eating dark chocolate, there are also some downsides.It Contains Caffeine
Dark chocolate contains 35 milligrams of caffeine per ounce compared to 145 milligrams for an 8-ounce cup of black coffee. Consider that if you’re trying to watch your caffeine intake or not hinder your ability to fall asleep at night.
It Can Increase the Risk of Kidney Stones
Dark chocolate contains a component found in many plants and animals called oxalates, which can increase the risk of kidney stones. If you’re prone to getting kidney stones you may want to watch your dark chocolate consumption.
It Can Bring on Migraines
Dark chocolate has been implicated in some migraines. However, there are also people who are prone to migraines and don’t seem to be affected by dark chocolate, so the jury is still out. If you have a tendency to get migraines you may want to cut dark chocolate out of your diet to see if it helps.
Moderation Is Key
As with any sweet treat, moderation is key. Some dark chocolates contain more sugar and fat than others, although it’s typically a healthy fat from cocoa butter. Generally the higher the percentage of cocoa the less sugar it will contain, but this is not always the case. Read the labels to ensure just what your dark chocolate contains. And strive to not exceed 1 ounce per day.Consult your healthcare practitioner if you’re concerned about caffeine, kidney stones, or migraines. For the best dark chocolate, shop at local chocolatiers, and buy organic and/or fair-trade whenever possible.
*Editor’s Note: The information in this article is intended for your educational use only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition and before undertaking any diet, supplement, fitness, or other health programs.
Ready to take control of your health? Download the Chopra App for personalized well-being guidance you can access anywhere.